Multitenancy with Axon
In cloud computing, multitenancy allows multiple application users to use the same resources while remaining totally separate from each other – logically and physically.
You see multitenancy at work in SaaS products, where there may be several customers using the same service, but are considered separate tenants.
For the purposes of this blog, we’ll imagine a hypothetical hotel management SaaS software that’s sold to customers as a managed service.
So what kind of multitenancy does Axon support to help you implement such a service?
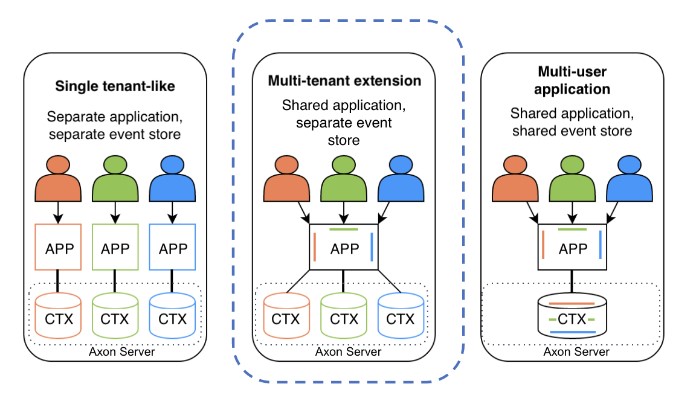
Historically, Axon has supported Single tenant-like and multi-user applications. However, for offering more flexible multi-tenant functionality a Multi-tenant extension was missing. Here’s why.
In the multi-user approach, you can store data from all tenants in one event store and logically separate the tenants’ data using frameworks like Spring Security.
But you’re limited. Suppose your customer needs to have data separated due to state or company policy? What if your customer requests their data to be wiped after terminating the service? By definition, event stores are immutable, meaning the state of the data cannot change after creation – creating an issue for these scenarios.
This rules out the multi-user approach.
So, what about the single-tenant-like approach?
Here you’d create an individual event store, or context, per customer. Great! Now your customers’ data is physically separated and can be permanently removed.
But there’s a downside: you’d need to deploy an application for every single tenant. That may not be an issue when your service is supporting a limited number of clients, but should your customer base grow, you’ll find this approach complicated and impractical.
Multitenant extension
As of Axon Framework 4.6+ and Axon Server 4.6+ the third approach is supported, which basically combines previously mention cases. Multiple users can use a single application and have their data physically separated in different event stores.
In this blog, we will consider how a single Axon Framework application can serve multiple event stores, or why you should set up a multi-tenant Axon Framework environment using the multitenancy extension.
The problem
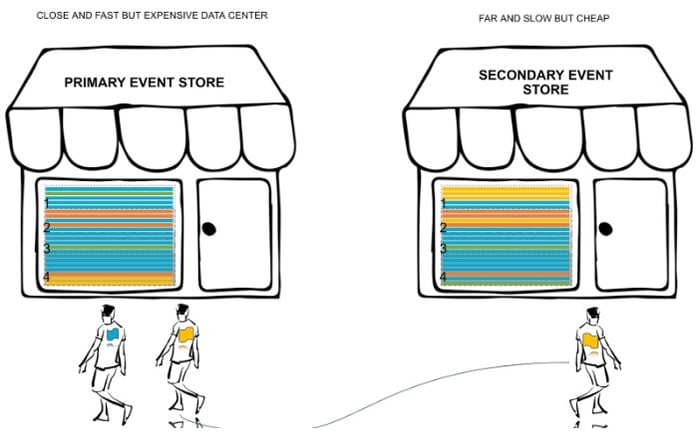
Let’s return to our hypothetical Hotel Management SaaS platform. If we were to use a single event store to store all of our customer's data, then the customers’ data would be scattered across different files. Review the picture below.

Suppose the blue tenant visits the event store to fetch his last five events. The event store would then need to open two files or segments. Opening files from the disk is an expensive operation. The situation becomes more convoluted for other tenants, whose data is now scattered across several segments. Suppose the green tenant now wants to fetch his last five events. Now the event store needs to open four files.
The situation further complicates when introducing secondary storage. Now the yellow tenant is pushed out to a different data center and a slow disk.
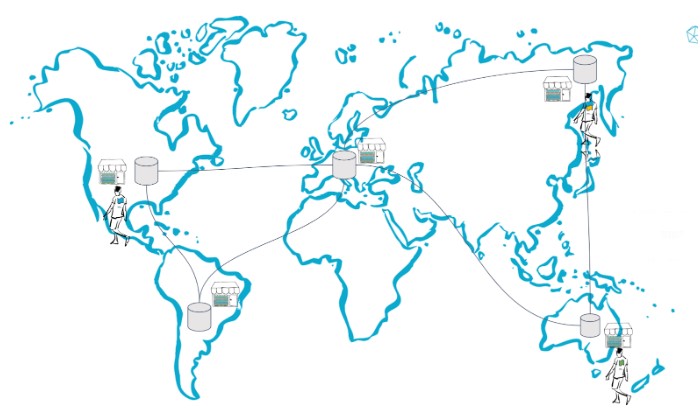
Another aspect you’d want to consider is multi-region fault tolerance. Fault tolerance is your system’s ability to endure a failure of some kind, but continue to operate properly. Let’s face it – failures happen!
Suppose you need to scale across regions then you would need to carry all the data, even if some tenants reside in one particular region, and their data should never be in some other region.
The solution
As hinted in the beginning, we resolve that the solution for our Hotel Management SaaS platform is implementing a multitenant extension and creating dedicated event stores (or context) for each customer.
Let's see how our event stores would look now.
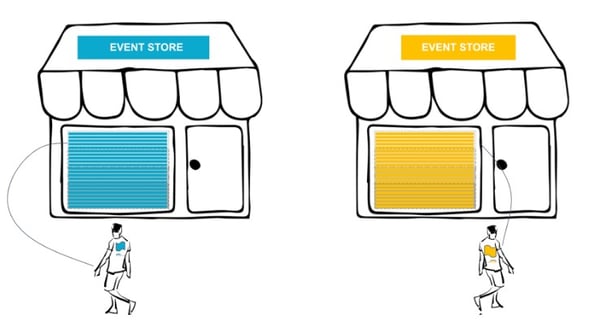
Each tenant visits his own event store, and there is no danger of his data being pushed or scattered by other more active tenants.
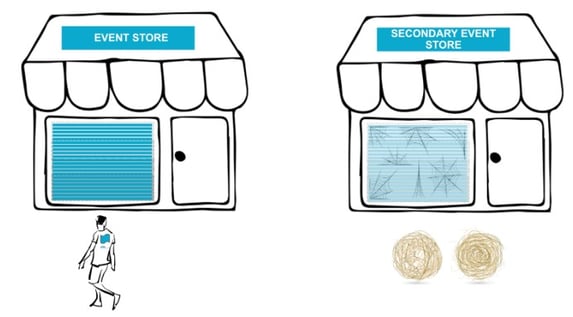
We may also select different disks to store data for each tenant and physically separate the data.
Let’s see how our multi-region looks now.
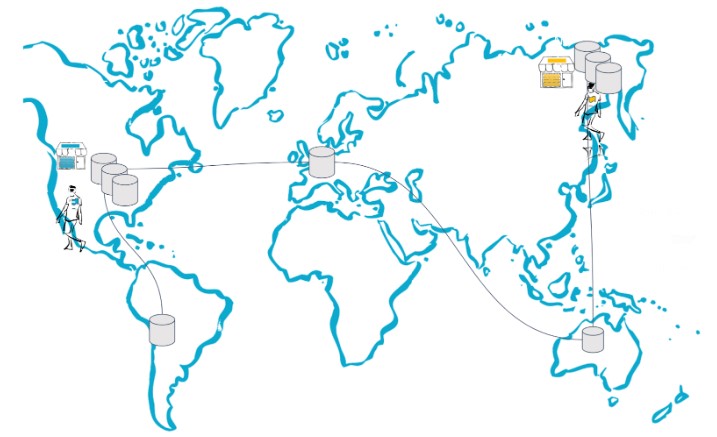
Tenant data remains close, but does not unnecessarily replicate across regions.
Now if your customer decides to leave our platform, we can simply remove their own event store along with all sensitive data. GDPR ✔️
Scalability
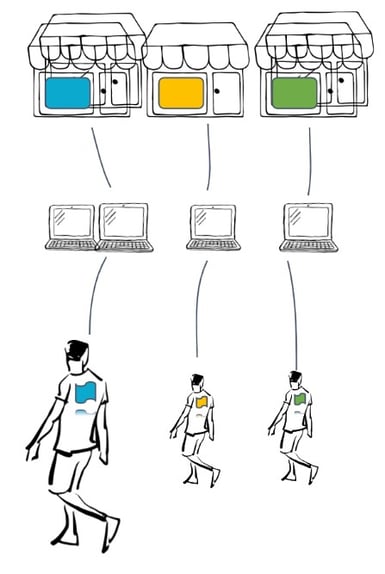
Another benefit of multitenant applications is the unlimited scalability options. Review the illustrations below.
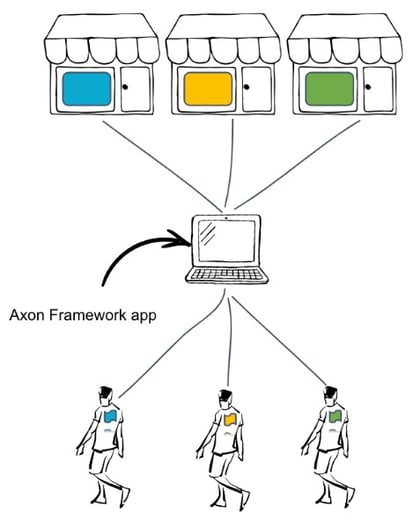
Multiple tenants using scaled Axon Framework application and their contexts replicated across multiple nodes.
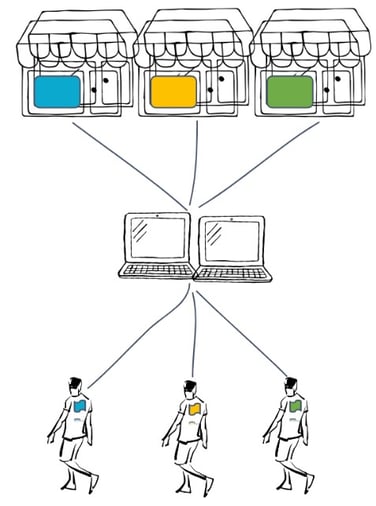
Separating premium customers with dedicated resources and deployed applications
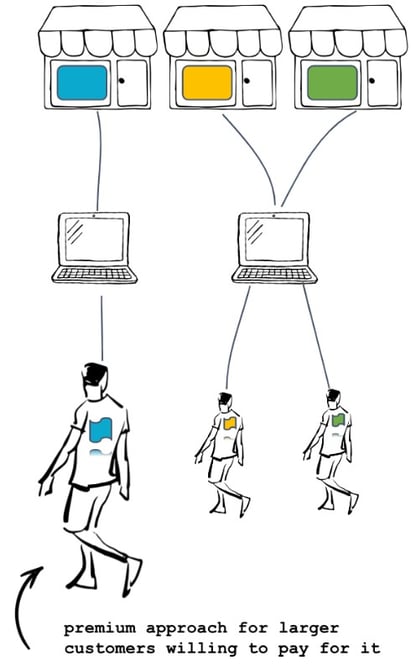
If the premium tenant grows even further, we can simply scale his application.
Summary
Multitenancy offers many benefits that can support data storage for multiple customers across multiple regions, but it’s not a silver bullet. Let’s compare:
| Single context | Multitenant - context per tenant |
| Initially less development Simple architecture - easier to understand Simplified DevOps Less configuration |
Easier to maintain over time Lower latencies Data closer to tenants Unlimited scaling options Ability to move and delete data Cheaper storage Data isolation (some clients might have Geo restrictions) |
| Harder to maintain over time Not able to delete data of single tenant Less scaling possibilities |
Initially more development More complex architecture Complex DevOps Complex configuration |
Should you go multitenant?
Answer the following questions:
- Is your product tenant-centric?
- Do your tenants need to interact with each other at all?
- Do you need to reduce the hosting costs of your SaaS product by offering a single application that can serve multiple, physically-separated clients?
- Do your clients’ data need to be stored separately from each other?
- Does your client’s data need to remain as close as possible for lower latency?
- Does your client need a premium service, which includes dedicated resources?
- Do you need to scale premium clients independently?
- Do you have strong GDPR requirements, but also use CQRS/Event Sourcing?
If you answered ‘yes’ to most of these questions, multitenancy might be the perfect approach for your product.
Further Reading and Code Examples
For more information on how to implement a multitenant application, take a look at the documentation of multitenancy extension and check out this demo application.

